Is your laptop battery draining faster than it used to? Does your system randomly shut down despite showing remaining charge? Power management issues can significantly impact your productivity and laptop lifespan. This comprehensive guide covers everything from quick fixes to advanced diagnostics for battery and power-related problems in Windows.
Understanding Windows Power Management
Modern Windows systems use sophisticated power management that involves multiple components working together:
Hardware Components:
-
Battery cells and charging circuitry
-
Power management IC (PMIC)
-
CPU and GPU power states
-
Display backlight and wireless radios
Software Components:
-
Windows power management drivers
-
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)
-
Power plans and profiles
-
Application power usage tracking
Common Power Issues like:
-
Inaccurate battery reporting
-
Rapid battery drain
-
Charging problems
-
Sleep/hibernate failures
-
Thermal throttling affecting performance
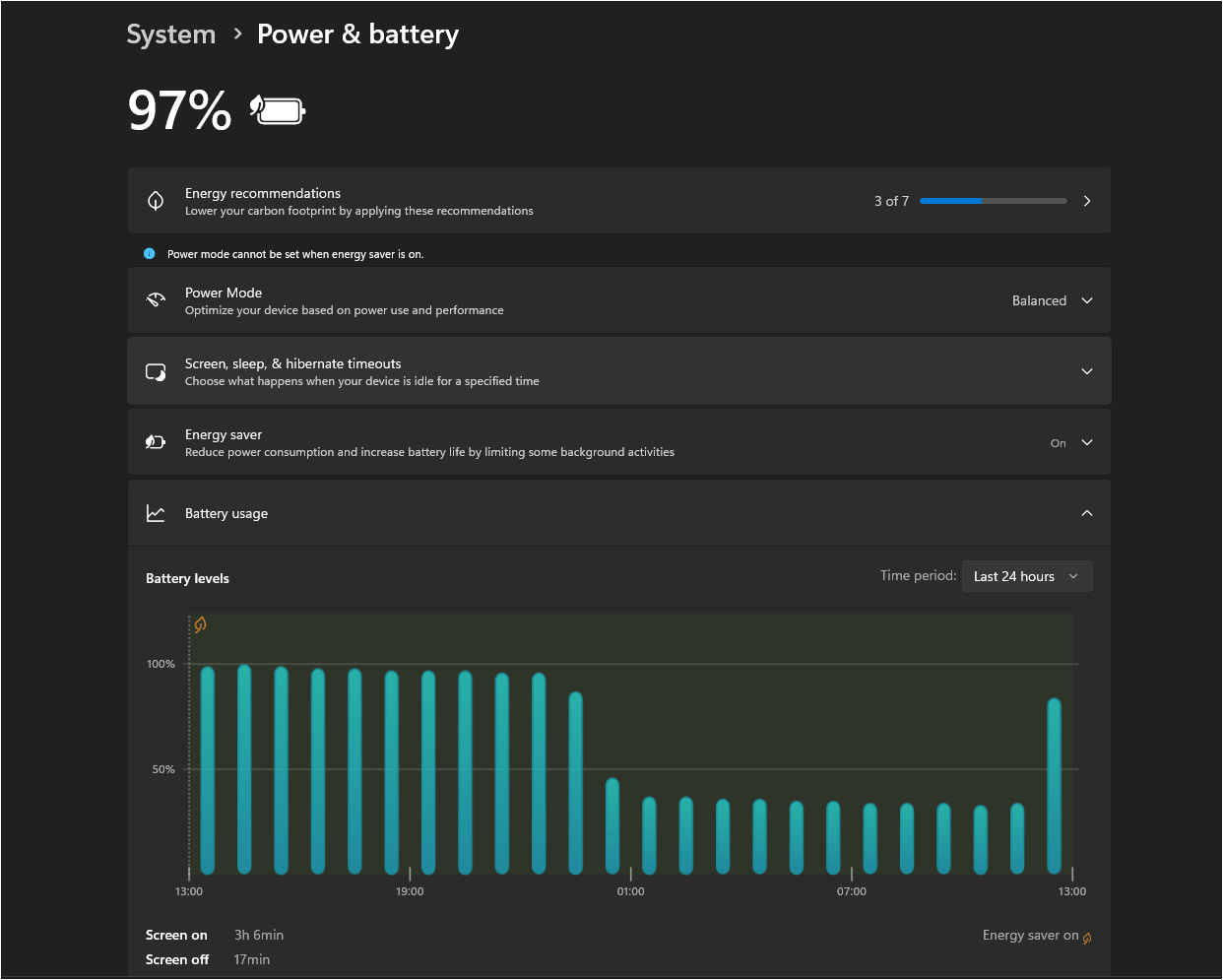
Quick Battery Diagnostics
Check Current Battery Health Using Windows Battery Report command:
-
Press
Win + Xand select "Windows PowerShell (Admin)" -
Type:
powercfg /batteryreport -
Press Enter and note the file location (usually
C:\Windows\system32\battery-report.html) -
Open the HTML file in your browser to view detailed battery information
The report shows:
-
Design capacity vs. full charge capacity
-
Battery usage patterns over the last 3 days
-
Battery life estimates
-
Charge/discharge cycles
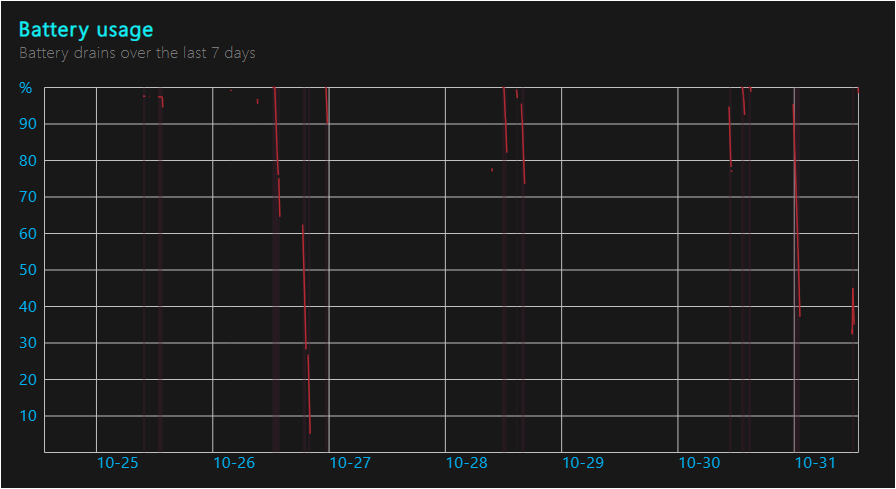
Power Efficiency Report:
-
In the same PowerShell window, type:
powercfg /energy -
Wait for the 60-second analysis to complete
-
Open the generated
energy-report.htmlfile -
Review warnings and errors related to power efficiency
Battery Icon and Notification Issues
If your battery icon is missing:
-
Right-click the taskbar and select "Taskbar settings"
-
Click "Turn system icons on or off"
-
Ensure "Power" is set to "On"
-
If still missing, restart Windows Explorer via Task Manager
-
Open Device Manager and disable then re-enable the Microsoft AC Adapter.
Incorrect Battery Percentage:
-
Often indicates driver issues or battery calibration problems
-
May show as "plugged in, not charging" when battery is full
-
Can display wildly inaccurate percentages (e.g., jumping from 50% to 10%)
Rapid Battery Drain Solutions
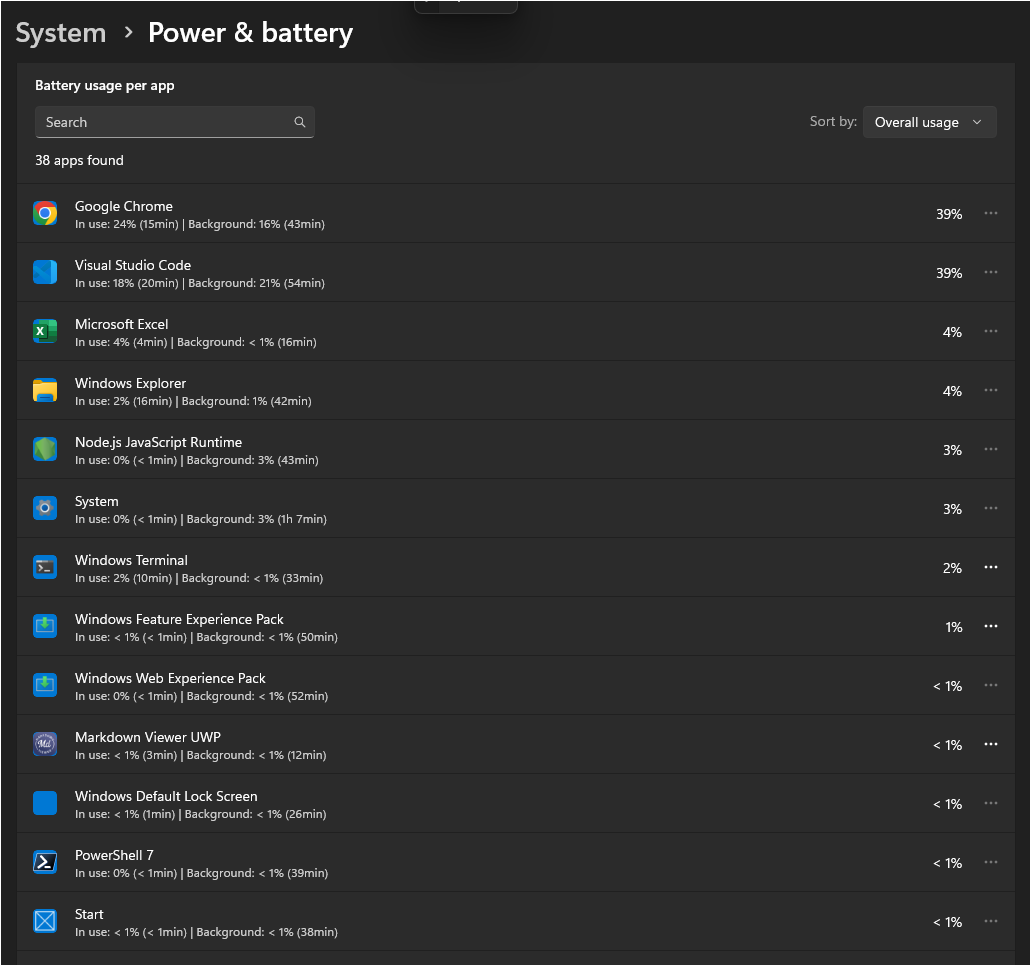
1. Identify Power-Hungry Applications
Using Task Manager:
-
Open Task Manager (
Ctrl + Shift + Esc) -
Click "More details" if in compact view
-
Go to the "Processes" tab
-
Click the "Power usage" column to sort by power consumption
-
Identify applications using "Very high" or "High" power
Using Settings App:
-
Go to Settings > System > Battery
-
Click "Battery usage by app"
-
Review which applications consume the most battery
-
Consider uninstalling or replacing power-hungry apps
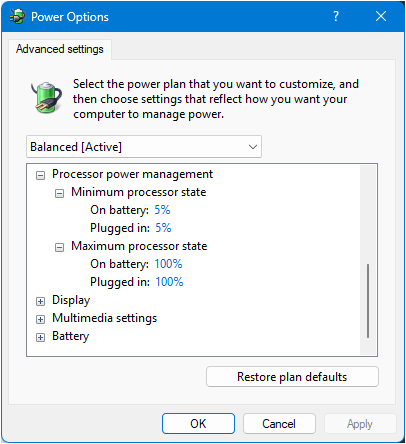
2. Optimize Power Plans
Access Power Options:
-
Right-click the battery icon in system tray
-
Select "Power Options"
-
Choose "Balanced" for everyday use or "Power saver" for maximum battery life
-
Click "Change plan settings" to customize
Advanced Power Settings:
-
Click "Change advanced power settings"
-
Key settings to optimize:
-
Hard disk: Set to turn off after 5-10 minutes on battery
-
Wireless adapter settings: Set power saving mode to "Maximum Power Saving"
-
Sleep settings: Configure appropriate sleep times
-
Processor power management: Reduce maximum processor state on battery (try 80-90%)
-
Display: Lower brightness timeout values
-
3. Manage Background Applications
Disable Startup Programs:
-
Open Task Manager > "Startup" tab
-
Disable unnecessary programs with "High" startup impact
-
Common culprits: Adobe updaters, Skype, Steam, Spotify
Background App Permissions:
-
Go to Settings > Privacy > Background apps
-
Turn off background access for apps you don't need running constantly
-
Keep essential apps like Mail, Calendar, and antivirus enabled
Windows Update Delivery:
-
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Advanced options
-
Click "Delivery Optimization"
-
Turn off "Allow downloads from other PCs" to save bandwidth and battery
Charging Problems and Solutions
1. Hardware-Related Charging Issues
Check Physical Connections:
-
Ensure charging cable is firmly connected
-
Inspect charging port for debris or damage
-
Try a different power outlet
-
Test with original charger if using third-party adapter
Charger Compatibility:
-
Verify wattage matches laptop requirements (check laptop label)
-
USB-C laptops may charge slowly with low-wattage phone chargers
-
Some laptops require proprietary charging connectors
2. "Plugged in, not charging" Fix
This common issue often indicates driver or calibration problems:
Update Battery Drivers:
-
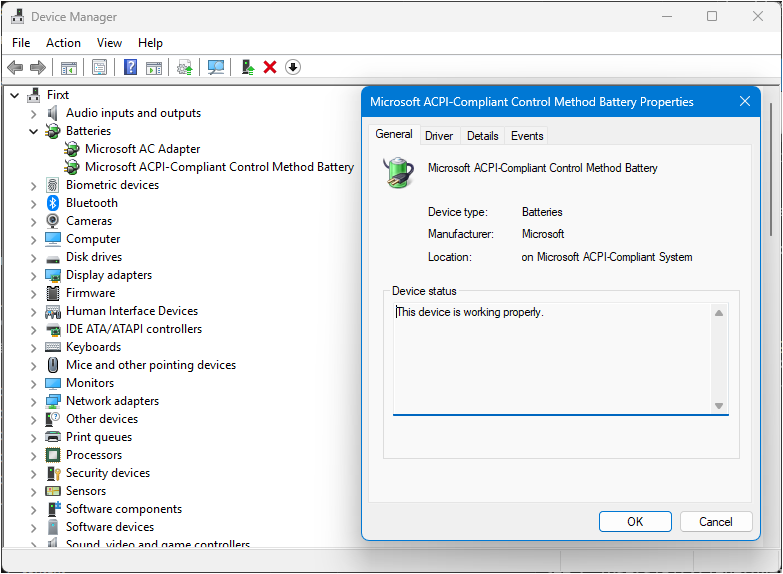
Open Device Manager (
Win + X> Device Manager) -
Expand "Batteries"
-
Right-click "Microsoft ACPI-Compliant Control Method Battery"
-
Select "Uninstall device"
-
Restart computer (Windows will reinstall the driver)
Reset Power Management:
-
Shut down laptop completely
-
Remove battery (if removable)
-
Hold power button for 30 seconds
-
Reconnect battery and charger
-
Power on normally
3. Calibrate Battery
Battery calibration helps Windows accurately report charge levels:
Manual Calibration Process:
-
Charge battery to 100%
-
Use laptop normally until battery reaches 5-10%
-
Let laptop hibernate/shut down automatically
-
Leave powered off for 2-3 hours
-
Charge back to 100% without interruption
-
Repeat this cycle 2-3 times if needed
BIOS-Level Calibration:
-
Some laptops have built-in calibration tools in BIOS/UEFI
-
Access during boot (usually F2, F12, or Del key)
-
Look for "Battery Calibration" or similar option
Sleep and Hibernate Issues
1. Sleep Problems
Computer Won't Sleep:
-
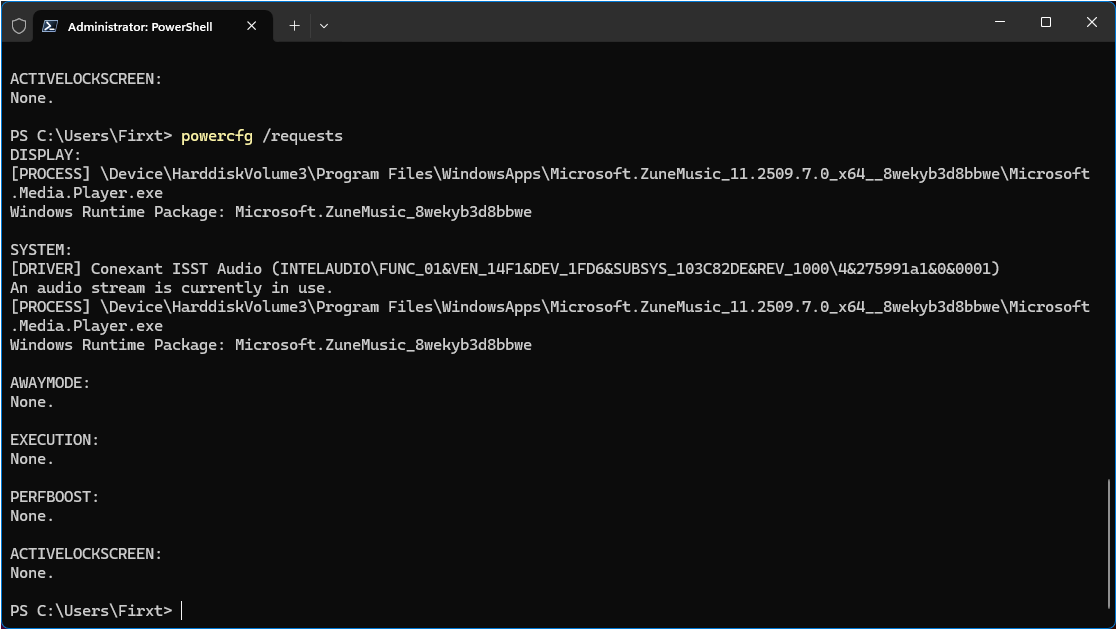
Open Command Prompt as Administrator
-
Type:
powercfg /requests -
This shows what's preventing sleep
-
Common culprits: network adapters, audio devices, running applications
Wake from Sleep Issues:
-
Check Device Manager for devices that can wake the computer
-
Right-click network adapter > Properties > Power Management
-
Uncheck "Allow this device to wake the computer" if causing problems
-
Also check USB devices, especially mice and keyboards
2. Hibernate Configuration
How to Enable Hibernation:
-
Open Command Prompt as Administrator
-
Type:
powercfg /hibernate on -
Press Enter
How to Optimize Hibernation:
-
Go to Control Panel > Power Options
-
Click "Choose what the power buttons do"
-
Set lid close action to "Hibernate" for maximum battery savings
-
Configure power button to hibernate instead of sleep
Reduce Hiberfil.sys Size:
-
In Admin Command Prompt, type:
powercfg /hibernate /size 50 -
This reduces hibernate file to 50% of RAM size
-
Saves disk space but may not hibernate all open applications
Advanced Power Troubleshooting
1. Driver and Firmware Updates
Update Power Management Drivers:
-
Visit laptop manufacturer's website
-
Download latest chipset and power management drivers
-
Install BIOS/UEFI updates (be cautious - only if needed)
-
Update graphics drivers which significantly impact battery life
Intel Power Management:
-
Install Intel Driver & Support Assistant
-
Ensure Intel Management Engine Interface is updated
-
Update Intel Dynamic Platform and Thermal Framework
2. Registry Fixes for Power Issues
Reset Power Settings (Registry):
-
Press
Win + R, typeregedit -
Navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power -
Delete the "User" folder (this resets all power customizations)
-
Restart computer
Note: This will reset all custom power settings to defaults.
3. Windows Power Troubleshooter
Run Built-in Troubleshooter:
-
Go to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot
-
Click "Additional troubleshooters"
-
Run "Power" troubleshooter
-
Follow recommended actions
Battery Health and Replacement
1. Understanding Battery Degradation
Normal Degradation Patterns:
-
Lithium batteries typically lose 20% capacity after 300-500 cycles
-
Degradation accelerates with age, heat exposure, and deep discharges
-
Capacity below 80% of original indicates replacement time
Check Cycle Count:
-
Use battery report:
powercfg /batteryreport -
Look at "Cycle count" in the report
-
Most laptop batteries rated for 300-1000 cycles
2. Extending Battery Lifespan
Best Practices:
-
Keep battery between 20-80% charge when possible
-
Avoid leaving laptop plugged in 24/7 (some manufacturers have built-in protection)
-
Store laptop with 50% charge if unused for extended periods
-
Avoid extreme temperatures (both hot and cold)
-
Use manufacturer's battery care software if available
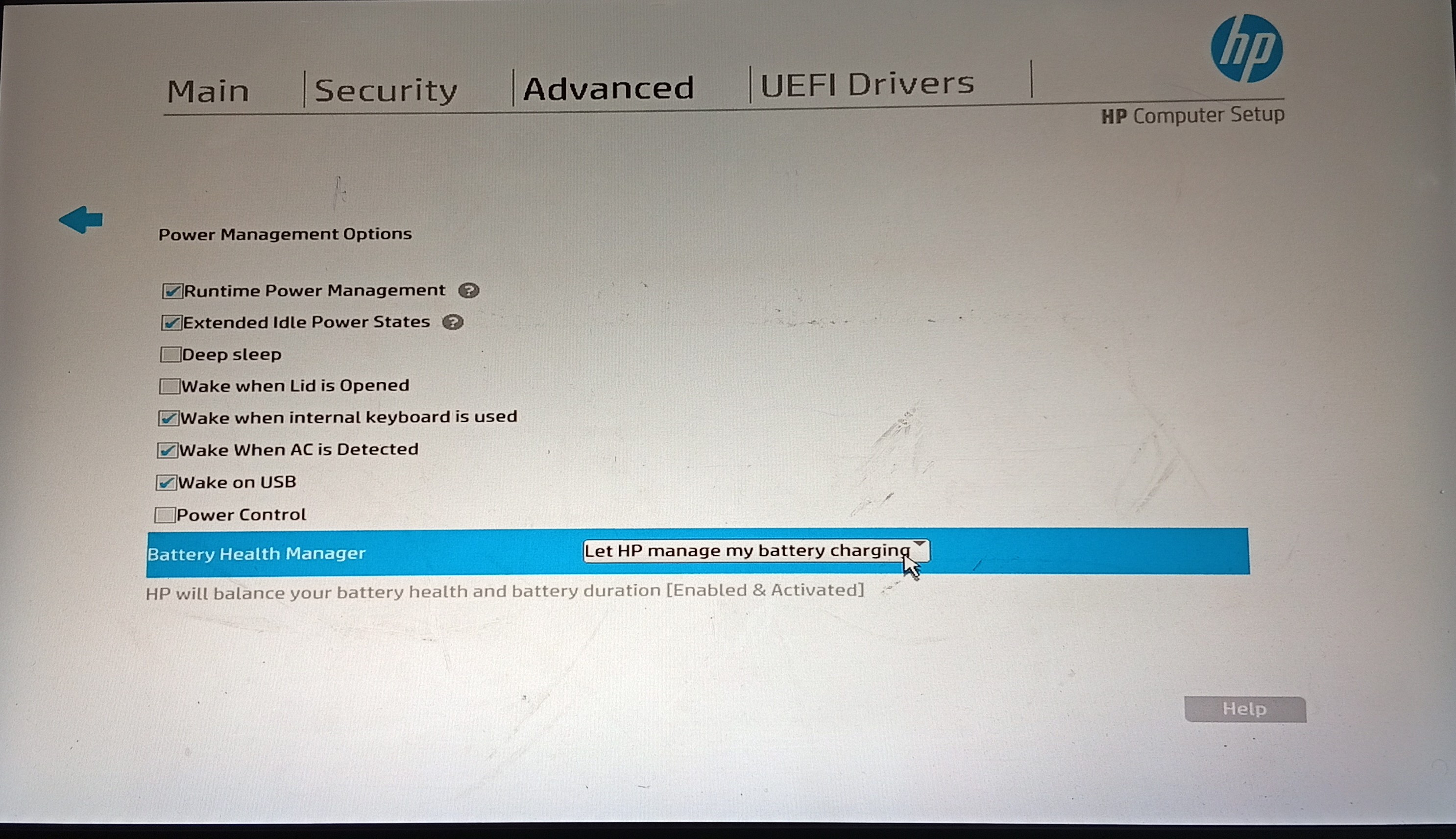
Manufacturer Battery Tools:
-
Lenovo Vantage (Battery Health settings)
-
Dell Power Manager (Battery optimization)
-
HP Smart (Battery health check)
-
ASUS Battery Health Charging
3. When to Replace Battery
Replacement Indicators:
-
Battery report shows <80% design capacity
-
Laptop shuts down unexpectedly with charge remaining
-
Battery swells (physical deformation)
-
Charging takes significantly longer than normal
-
Battery gets very hot during charging
Replacement Options:
-
Official manufacturer batteries (recommended for warranty coverage)
-
Third-party batteries (cheaper but variable quality)
-
Professional battery replacement service
-
DIY replacement (check if battery is user-replaceable)
Thermal Management and Performance
1. Thermal Throttling Issues
Identifying Thermal Problems:
-
Use HWiNFO64 or Core Temp to monitor CPU temperatures
-
Normal: <70°C, Concerning: >80°C, Throttling: >90°C
-
GPU temperatures should stay below 85°C under load
Solutions for Overheating:
-
Clean laptop vents and fans with compressed air
-
Use laptop cooling pad
-
Reduce CPU maximum processor state in power options
-
Lower screen brightness and disable keyboard backlighting
-
Close unnecessary applications
2. Performance vs. Battery Balance
Balanced Performance Settings:
-
Set CPU max state to 90% on battery power
-
Enable adaptive brightness
-
Use integrated graphics instead of dedicated GPU when possible
-
Reduce display refresh rate if laptop supports variable refresh
Ultra Power Saving Mode:
-
Some laptops have dedicated ultra-low-power modes
-
Windows 10/11 "Battery Saver" mode
-
Reduces background activity and lowers performance
-
Can extend battery life by 20-30%
Monitoring and Maintenance
1. Regular Battery Monitoring
Weekly Checks:
-
Review battery usage by app in Settings
-
Check for Windows updates affecting power management
-
Monitor charging behavior for irregularities
Monthly Maintenance:
-
Generate battery report to track degradation
-
Clean laptop vents and check for dust buildup
-
Review and update power plans based on usage patterns
Quarterly Deep Checks:
-
Run full power efficiency diagnosis
-
Update all drivers and firmware
-
Perform battery calibration if needed
2. Useful Third-Party Tools
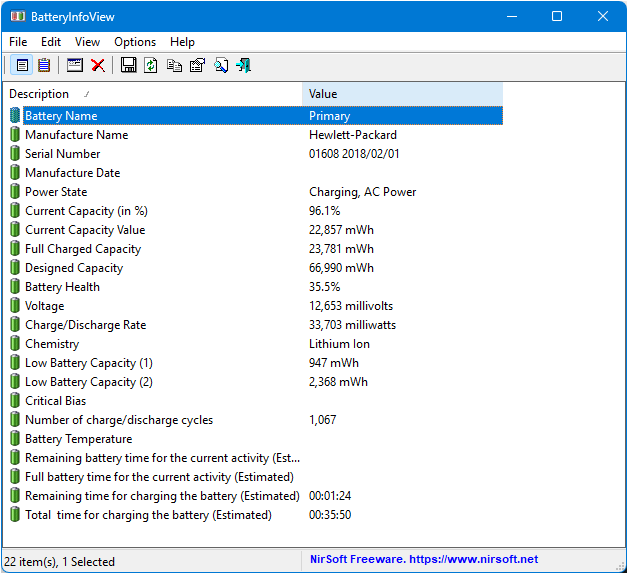
Battery Monitoring:
-
BatteryInfoView: Detailed battery statistics
-
BatteryMon: Real-time battery monitoring and logging
-
HWiNFO64: Comprehensive hardware monitoring including power draw
Power Management:
-
ThrottleStop: Advanced CPU power management
-
MSI Afterburner: GPU power monitoring and control
-
Process Lasso: Automatic power plan switching based on applications
Emergency Power Solutions
1. Maximum Battery Extension
When Battery is Critical:
-
Enable "Battery Saver" mode immediately
-
Close all non-essential applications
-
Disconnect all USB devices
-
Turn off WiFi and Bluetooth if not needed
-
Lower screen brightness to minimum usable level
-
Switch to airplane mode if network not required
Emergency Shutdown:
-
Save all work immediately
-
Use hibernation instead of sleep
-
Consider partial shutdown of unnecessary Windows services
2. Portable Charging Solutions
Power Bank Options:
-
USB-C Power Delivery banks (45W+ for laptops)
-
AC power banks with standard outlets
-
Car inverters for mobile computing
Charging Optimization:
-
Charge laptop while powered off for fastest charging
-
Use original charger when possible
-
Remove battery-draining peripherals while charging
Troubleshooting Specific Error Messages
"Consider replacing your battery"
This Windows notification indicates significant battery degradation:
-
Generate battery report to confirm actual capacity
-
Check warranty status if laptop is relatively new
-
Continue using laptop plugged in if replacement not immediate
-
Monitor for swelling or unusual heating
"Your battery is experiencing problems"
Usually indicates driver or communication issues:
-
Update battery drivers via Device Manager
-
Run Windows troubleshooter
-
Check for BIOS updates
-
Reset power management settings
When to Seek Professional Help
Consider professional service if:
-
Battery is physically swollen or damaged
-
Laptop randomly shuts down despite showing charge
-
Charging port appears damaged or loose
-
Multiple troubleshooting attempts have failed
-
System won't power on at all
-
You smell burning or see sparks (stop using immediately)
Professional services can:
-
Safely replace internal batteries
-
Diagnose complex power delivery issues
-
Repair charging ports and power circuits
-
Update firmware that requires special tools
Conclusion
Battery and power issues can significantly impact your Windows laptop experience, but most problems can be resolved through systematic troubleshooting. Start with software solutions like driver updates and power plan optimization before considering hardware replacement.
Regular monitoring and maintenance are key to preventing power problems. Keep your system updated, monitor battery health quarterly, and maintain good charging habits to extend battery lifespan.
Remember that battery degradation is normal over time, and replacement is part of regular laptop maintenance. The key is recognizing when performance issues are due to failing hardware versus software configuration problems.
When in doubt, the Windows battery report is your best diagnostic tool. It provides concrete data about battery health and usage patterns that can guide your troubleshooting efforts.
